/\/\o\/\/ PowerShelled
This blog has moved to http://ThePowerShellGuy.com Greetings /\/\o\/\/ $AtomFeed = ("Atom.xml")$PreviousItems = (" Monad Really Does Rock "," Passing (not so) mandatory Parameters to WMI metho... "," Saving a WMI instance to a XML-file from MSH "," MSH Orphan share remover Tool "," MSH Welcome screen "," Read the raw Monad XML helpfiles "," MSH prompt-User function with Help "," Monad IRC Bot "," Getting performanceMonitor info from Monad "," Monad -and More bytes with -band = shorter script "," ")
Friday, December 23, 2005
Using ADO to get data from Excel to Dataset in Monad.
If you got an Excel sheet with Data, you can use the Excel.Application COM-object to get data from it, but you can also use ADO and a Dataset for this as I will show in this post.
For this example, I made a New Excel Sheet and entered the following Data and did save it as Puters.XLS.
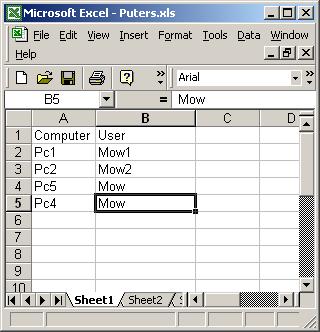
Now we have the Excel sheet we will use Monad to get the Data.
First let's make a connection to the Excel Sheet:
$excel = "C:\Puters.xls"
# Make the Connection :
$ConnString = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=$excel;Extended Properties=Excel 8.0;"
$Conn = new-object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection($connString)
# Open the Connection
$conn.open()
# Make the Connection :
$ConnString = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=$excel;Extended Properties=Excel 8.0;"
$Conn = new-object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection($connString)
# Open the Connection
$conn.open()
then we will get the Available Tables (there will be three as every sheet will be a Table, and Excel starts standard with 3 sheets)
# Get the available Tables
$Tables = $Conn.GetOleDbSchemaTable([System.Data.OleDb.OleDbSchemaGuid]::tables,$null)
$Tables = $Conn.GetOleDbSchemaTable([System.Data.OleDb.OleDbSchemaGuid]::tables,$null)
Now we have got the Table(s) ready we can make a Select Query to get back the Data,
I will use Select * and no filter as we will use the dataset for this later.
# make a Command to get all data of the first table (Sheet)
$cmd = new-object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand("Select * from [$($tables.rows[0].TABLE_NAME])",$Conn)
$cmd = new-object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand("Select * from [$($tables.rows[0].TABLE_NAME])",$Conn)
Now we have the Command and the Connection ready we can make a DataAdapter that uses the Command to fill our DataSet:
# Load a DataAdapter with the Select Command.
$da = new-object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter($cmd)
# Fill a DataSet from the Data Adapter
$ds = new-object System.Data.dataset
$da.fill($ds)
$da = new-object System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataAdapter($cmd)
# Fill a DataSet from the Data Adapter
$ds = new-object System.Data.dataset
$da.fill($ds)
So now the DataSet is filled, we are ready to use the data from Excel.
As the data is in a DataSet now we can use DB methods like filters and Sorts on the Data as shown in the Examples Below:
# get the Tables
$ds.tables
# get all Row's where User is Mow1
$ds.tables[0].select("user = 'Mow1'")
# Some More Selects and Sorts
# As is :
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0]
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc1 Mow1
Pc2 Mow2
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
# Only PC's of user Mow
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select("user = 'Mow'")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
# Only users ending with a 2
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select("user like '*2'")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc2 Mow2
# All records Sorted Ascending
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select($null,"Computer ASC")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc1 Mow1
Pc2 Mow2
Pc4 Mow
Pc5 Mow
# All Records Descending
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select($null,"Computer DESC")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
Pc2 Mow2
Pc1 Mow1
$ds.tables
# get all Row's where User is Mow1
$ds.tables[0].select("user = 'Mow1'")
# Some More Selects and Sorts
# As is :
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0]
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc1 Mow1
Pc2 Mow2
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
# Only PC's of user Mow
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select("user = 'Mow'")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
# Only users ending with a 2
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select("user like '*2'")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc2 Mow2
# All records Sorted Ascending
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select($null,"Computer ASC")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc1 Mow1
Pc2 Mow2
Pc4 Mow
Pc5 Mow
# All Records Descending
MSH C:\> $ds.tables[0].select($null,"Computer DESC")
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
Pc2 Mow2
Pc1 Mow1
To Finish this entry, I will show you how you can save to and Reload the Generated DataSet to and from an XML-file.
# Save this Dataset as XML Document:
$sw = new-object system.io.streamwriter("C:\Puters.xml")
$ds.WriteXml($sw)
$sw.close()
# Load XML document into new dataset :
$sr = new-object system.io.streamreader("C:\Puters.xml")
$ds2.ReadXml($sr)
MSH C:\> $ds2.tables
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc1 Mow1
Pc2 Mow2
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
$sw = new-object system.io.streamwriter("C:\Puters.xml")
$ds.WriteXml($sw)
$sw.close()
# Load XML document into new dataset :
$sr = new-object system.io.streamreader("C:\Puters.xml")
$ds2.ReadXml($sr)
MSH C:\> $ds2.tables
Computer User
-------- ----
Pc1 Mow1
Pc2 Mow2
Pc5 Mow
Pc4 Mow
As you can see having this data in a Dataset has advantages over the data in Excel as you directly query and filter the DataSet.
Also you don't need the Excel COM object as you make a OBDC connection to the Excel Data.
Also there a lot more possibilities with the DataSet, for example add relations to other tables etc.
what make this a very powerfull way to get at your Excel Data.
(Same goes for MsAccess for example) for SQL you will use the System.Data.SqlClient namespace, but the methods are almost the same, I will blog about that later.
gr /\/\o\/\/

